The wood pile at the back has grown and we think about setting it alight and burning everything so we can tidy it up and create more space for more wood and brush.
The Wood Pile is actually a large store of Carbon and when we burn it, we release all that Carbon as CO2 which we know is not good for the environment. Let’s examine if there is much CO2 trapped in the Burn Pile:
Estimated Size: 80 yards long x 20 feet deep by 9 feet tall on average. The burn pile is semi circular, but let’s assume the 80 yards is in a straight line.
| Volume | 43,200 | cuft |
| Weight | 1,396,440 | lbs 698 tons |
| CO2 | 2,225,880 | lbs |
| Hauling CO2e | 12,728 | lbs |
| 1,119 | tons CO2 emitted if we burn the pile | |
| If Wood Pile is 100% wood | ||
| Equivalent to | 339 | Humans living, driving, eating, buying stuff, electricity, gas – for one year (All the CO2 you would emit in a year) |
| 2,743,392 | miles driven in a Toyota Camary 3.5 liter car | |
| If Wood Pile is 50% wood | ||
| Equivalent to | 169 | Humans living, driving, eating, buying stuff, electricity, gas – for one year |
| 1,379,495 | miles driven in a Toyota Camary 3.5 liter car | |
| If Wood Pile is 25% wood | ||
| Equivalent to | 84 | Humans living, driving, eating, buying stuff, electricity, gas – for one year |
| 697,547 | miles driven in a Toyota Camary 3.5 liter car | |
What we Plan to do:
The wood will rot and degrade over time releasing almost all this carbon as CO2 so there is an argument that not setting the burn pile alight will do little to save the carbon trapped within it. We should really be burying the burn pile to trap the carbon underground.
However, it seems right to not burn the pile and release all that CO2 in one big hit, instead, let it rot over the next 5 -10 years and release CO2 slowly.
Details of calculations
Toyota Camary with 3.5 liter V6 emits 0.37 Metric Tons of CO2 per 1000 miles driven. This is 0.408 tons.
How much carbon dioxide is stored in my wood product?
Carbon dioxide isn’t stored in wood, per se. Carbon is stored in wood—and if that carbon were released into the atmosphere, it would combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. Therefore, we can calculate and report an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide stored in the wood.
Carbon has a molecular weight of 12. Oxygen has a molecular weight of 16. Therefore, carbon dioxide—one carbon and two oxygens—has a molecular weight of 44.
![]()

So, for every 12 pounds of carbon we’re storing in wood, that’s equivalent to 44 pounds of carbon dioxide that would otherwise occur in the atmosphere. Our calculations above showed that one cubic foot of Douglas fir-larch contains 15 lb of carbon. How much carbon dioxide is this equivalent to?
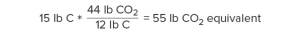
Every cubic foot of Douglas fir-larch stores the equivalent of 55 lb of carbon dioxide!
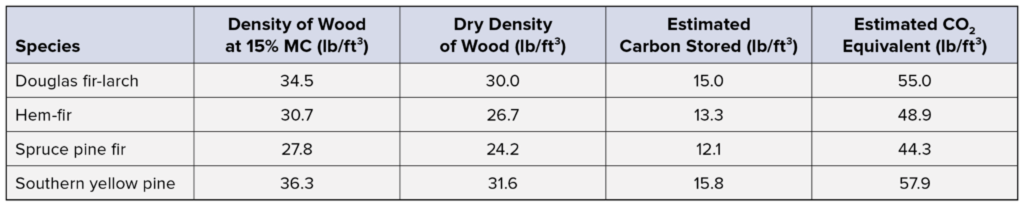
A summary of this data for common structural wood species is provided in the table below. For reference, burning one gallon of gasoline produces about 20 lb of carbon dioxide.2
Adapted from:
Dovetail Partners, Inc. (2013). Carbon in Wood Products – The Basics.